Cryptocurrency Posts
Crypto Briefing
TRM Labs' funding boost highlights the growing importance of AI in enhancing security measures and combating financial crimes globally.
The post Goldman-backed TRM Labs closes $70 million series C at $1 billion valuation appeared first on Crypto Briefing.
BitMine's approach highlights the volatility inherent in crypto investments, emphasizing the need for long-term strategies over short-term gains.
The post Tom Lee defends BitMine’s $6B in unrealized ETH losses as a feature not a flaw appeared first on Crypto Briefing.
UBS's exploration of crypto access for clients may accelerate digital finance adoption, influencing global banking strategies and competition.
The post UBS considers crypto offerings and tokenized deposit products for clients appeared first on Crypto Briefing.
Binance's Bitcoin conversion for SAFU may enhance user trust and market stability, reflecting a strategic shift towards decentralized assets.
The post Binance completes second batch of Bitcoin conversion, acquires $100M in BTC appeared first on Crypto Briefing.
Tether's reduced fundraising highlights investor skepticism, potentially impacting its market perception and future financial strategies.
The post Tether scales back $20B fundraising bid amid valuation concerns: Report appeared first on Crypto Briefing.
Bitcoin Magazine
Bitcoin Magazine

UBS to Build Digital-Asset Infrastructure, Eyes Bitcoin Services for Individuals
UBS Group AG is exploring ways to offer bitcoin and crypto access to individual clients, CEO Sergio Ermotti said during the bank’s earnings call on Wednesday.
Ermotti said the Zurich-based lender is building the core infrastructure needed for digital-asset services while evaluating targeted products, ranging from crypto access for wealthy clients to tokenized deposit solutions for corporate customers.
“We are building out the core infrastructure and exploring targeted offerings from crypto access for individual clients to tokenized deposit solutions for corporates,” Ermotti said.
The UBS chief stressed the bank does not plan to be a first mover in blockchain-based technology.
Instead, UBS is pursuing what Ermotti described as a “fast follower” strategy in tokenized assets, with expansion expected to unfold over the next three to five years alongside its traditional banking business.
It was reported last month that UBS is in the process of selecting partners for a crypto offering aimed at some of its high-net-worth clients, marking a shift for a bank that has historically taken a cautious stance on virtual tokens.
Like many global lenders, UBS has so far focused its digital-asset work on blockchain infrastructure for tokenized funds and payments.
Banks have generally moved slowly into areas like crypto trading, in part due to stricter capital requirements under the Basel III framework.
Other European banks like UBS exploring bitcoin
Other banks are also starting to embrace bitcoin and crypto offerings. DZ Bank recently secured MiCAR approval and will roll out its “meinKrypto” platform across cooperative banks, allowing customers to trade and custody Bitcoin and other digital assets directly within existing banking apps, while also joining a consortium developing a regulated euro stablecoin.
Also, the Sparkassen-Finanzgruppe plans to launch Bitcoin and crypto trading for private customers by the summer of 2026, with technical support from DekaBank, marking a reversal from its earlier skepticism toward digital assets and crypto.
Also earlier this week, ING Deutschland, one of Germany’s largest retail banks, said they will began offering retail clients access to cryptocurrency-linked exchange-traded notes (ETNs) and products, allowing customers to gain exposure to bitcoin and other crypto directly through their existing securities accounts.
According to information published on ING’s website, the products are physically backed exchange-traded instruments issued by established asset managers including the likes of 21Shares, Bitwise, and VanEck.
This post UBS to Build Digital-Asset Infrastructure, Eyes Bitcoin Services for Individuals first appeared on Bitcoin Magazine and is written by Micah Zimmerman.
Bitcoin Magazine

Strategy ($MSTR) Plummets 8% As Bitcoin Hits One‑Year Lows
Shares of Strategy plunged today, dipping more than 8% in trading as Bitcoin traded at new one-year lows and crypto risk assets came under renewed pressure.
The decline pushed MSTR’s share price to levels not seen since late 2024, deepening a multi‑month downtrend that has left the stock among the worst performers on the Nasdaq this year.
Bitcoin’s slump — dipping below key technical thresholds over the weekend and early week — has reverberated through markets, hitting crypto‑linked equities especially hard.
Shares of major crypto platforms, like Robinhood and Circle also lost ground, highlighting the increasing correlation between Bitcoin prices and related stocks.
With over 713,000 Bitcoins on its balance sheet, purchased at an average cost near $76,000 per coin, Strategy is grappling with unrealized losses after Bitcoin’s recent slide below that level.
Despite price dips, Chairman Michael Saylor has made it clear that Strategy won’t be selling its Bitcoin — and in fact is doubling down on purchases even as the market dips, signaling his intent to keep accumulating more.
In his messaging, he’s basically said he’s comfortable with holding and adding even on weakness, not cashing out when prices fall.
Strategy bought more bitcoin last week
Earlier this week, Strategy said it purchased 855 bitcoin for about $75.3 million, paying an average price of $87,974 per BTC, according to a Monday filing.
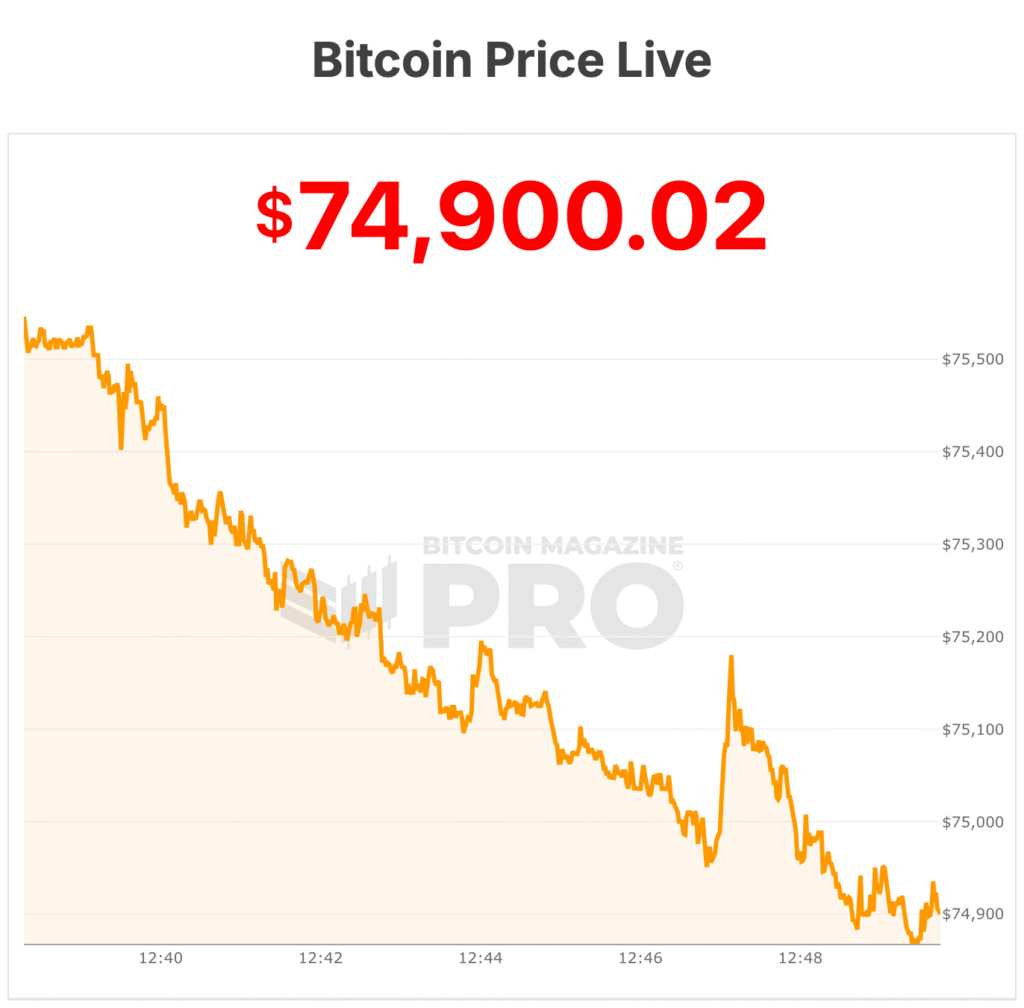
The acquisition came just days before bitcoin fell below $75,000 over the weekend on some rapid selling, briefly pushing Strategy’s treasury close to $1 billion in unrealized losses.
Now, the price of bitcoin is below those levels near $74,000.
The company now holds 713,502 BTC, acquired for roughly $54.26 billion at an average cost of $76,052 per coin.
Last week’s purchase was fully funded through the sale of common stock, following Strategy’s ongoing capital-raising approach to finance bitcoin buys. The purchase of 855 bitcoin was significantly smaller compared to prior company purchases.
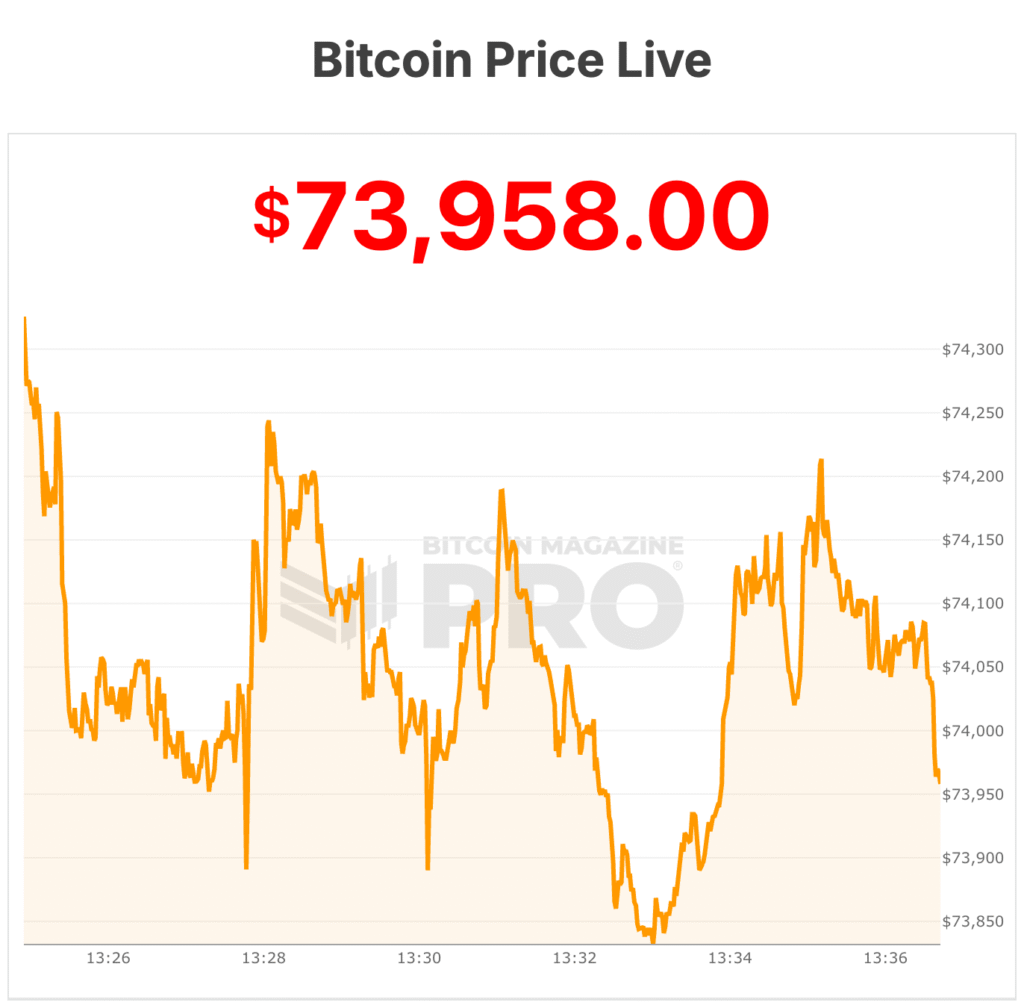
At the time of writing, bitcoin’s price dropped below $74,000 today, its lowest level in a year. The bitcoin price has now retraced more than 40% from its all‑time highs reached in late 2025.
Prior to today, the one-year low for the bitcoin price was $74,747. Strategy shares started the day at $139.66, but are currently trading at $128.87. The shares 52-week high was around $450 per share.
This post Strategy ($MSTR) Plummets 8% As Bitcoin Hits One‑Year Lows first appeared on Bitcoin Magazine and is written by Micah Zimmerman.
Bitcoin Magazine

Bitcoin Price Plunges 40% From All-Time Highs to One-Year Lows
Bitcoin’s price dropped below $75,000 today, its lowest level in nearly a year, as global crypto markets endured a sustained wave of selling triggered by broader financial stresses and shifting investor appetite.
The bitcoin price has now retraced more than 40% from its all‑time highs reached in late 2025. According to Bitcoin Magazine Pro data, the one-year low for the bitcoin price is $74,747. Bitcoin is dancing near that number.
Recent trading data showed Bitcoin price slipping through key technical support levels, driving forced liquidations across derivatives markets and intensifying downside price pressure. Over roughly the past 24 hours, around $2.56 billion in Bitcoin positions were liquidated, according to market data.
This follows weeks of risk‑off sentiment across global asset classes.
The downturn in cryptocurrencies has coincided with stress in other markets like precious metals, tech sell-offs, and losses in equities.
Institutional players report losses as policy signals remain dubious
The market slide has had tangible impacts on key industry participants. Galaxy Digital, a major crypto investment firm led by Michael Novogratz, reported a $482 million loss for the fourth quarter of 2025, earlier today.
The firm attributed this to the decline in digital asset prices and a sharp drop in trading volumes, which fell more than 40% from the prior quarter. Galaxy’s stock traded lower following the earnings release, reflecting investor concern about the broader bitcoin price and crypto downturn.
Also, Bitcoin price currently trades below $76,000, which is roughly the average price at which Strategy acquired a portion of its BTC holdings and well below the cost of many of its accumulated coins.
Since Strategy owns hundreds of thousands of bitcoins at higher average purchase prices, the current market value is less than what was paid for much of its inventory, leaving a significant portion of its holdings “underwater.”
Market participants have also pointed to U.S. monetary policy developments as a significant driver of the sell‑off.
The recent nomination of Kevin Warsh as chair of the U.S. Federal Reserve by President Donald Trump has prompted forecasts of tighter monetary conditions.
A strengthening U.S. dollar in response to monetary policy shifts has also weighed on Bitcoin. A firmer dollar typically makes non‑yielding assets like Bitcoin less attractive, reducing inflows from investors seeking currency‑neutral hedges. Analysts noted that the dollar’s recent performance provided technical headwinds that amplified the crypto market’s decline.
The Trump administration has continued to engage with industry leaders on digital asset policy, including efforts to advance regulatory clarity through legislation such as the Digital Asset Market Clarity Act.
This dialogue has really slowed down over the last couple of months, it has not yet translated into stabilizing price action amid current conditions.
Bitcoin price in genuine ‘crypto winter’
Despite this, Bitwise CIO Matt Hougan said in a recent memo that the crypto market has been in a genuine “crypto winter” since early 2025, rather than experiencing a short-lived correction.
Hougan highlighted that bearish sentiment remains strong, as evidenced by the Crypto Fear and Greed Index, which shows near all-time fear levels despite positive developments like the appointment of a bitcoin-friendly Fed chair.
Hougan noted that institutional flows helped mask the severity of the downturn. U.S. spot bitcoin ETFs and digital asset treasury vehicles purchased over 744,000 BTC during this period—roughly $75 billion in demand — cushioning bitcoin price’s drawdown, which he estimated could have reached nearly 60% without this support.
He compared the current environment to previous downturns in 2018 and 2022, where markets remained depressed despite incremental positive news.
Looking ahead, Hougan suggested that crypto winters often end not with exuberance but with exhaustion. In his words, “It’s always darkest before the dawn.”
Bitcoin price is currently at $74,800, with a 24-hour trading volume of 55 B. BTC is -5% in the last 24 hours. It is currently -5% from its 7-day all-time high of $78,994.
This post Bitcoin Price Plunges 40% From All-Time Highs to One-Year Lows first appeared on Bitcoin Magazine and is written by Micah Zimmerman.
Bitcoin Magazine

Bitcoin-Treasury The Smarter Web Company Listed on London Stock Exchange
The Smarter Web Company began trading on the Main Market of the London Stock Exchange today, marking a major milestone for the UK-based firm as it continues to position itself as Britain’s largest publicly listed bitcoin holder.
The company’s shares debuted under the ticker SWC at 43p. The uplisting follows the company’s initial public offering on the Aquis Exchange in April 2025, where it went on to become the UK’s best-performing equity that year.
Founded in 2009 by chief executive Andrew Webley, The Smarter Web Company began as a web design agency focused on building bespoke, mobile-friendly websites for small and medium-sized businesses.
In 2025, the firm pivoted toward a bitcoin treasury strategy, deploying capital into bitcoin as what it describes as “digital capital” on its balance sheet.
Today, The Smarter Web Company holds 2,674 bitcoin, making it the largest UK public company by bitcoin holdings and the 29th largest globally among public firms.
According to The Smarter Web Company, roughly £221 million of investor capital has been used to acquire bitcoin at an average price of just over $111,000 per coin.
Bitcoin was trading near $77,000 on Tuesday, down significantly from its peak above $120,000 last year.
Speaking at the London Stock Exchange opening ceremony, Webley said the Main Market listing represents the next stage in building a long-term British public company aligned with Bitcoin. “Moving to the Main Market of the London Stock Exchange marks the next significant milestone in that journey,” Webley said. “I am committed to building a British success story that contributes to the UK economy and demonstrates how bitcoin can be used as digital capital.”
Webley also reiterated his ambition for the company to enter the FTSE 250, potentially as early as the third quarterly rebalance of 2026, with longer-term aspirations to eventually reach the FTSE 100.
The United Kingdom’s version of Strategy
The Smarter Web Company’s strategy has drawn comparisons to U.S.-based firm Strategy, which pioneered the corporate bitcoin treasury model.
While a growing number of companies have since adopted similar approaches, Webley has argued that volatility is an inherent feature of the strategy rather than a flaw.
Despite its recent decline from a peak market capitalization of over £1 billion, Webley recently said the company plans to continue accumulating bitcoin regardless of price. The firm spent about £220 million accumulating their bitcoin, while its shares have plunged about 95%.
Webley argues the strategy is long-term, noting the company has increased its bitcoin holdings per share despite the downturn and plans to seek more institutional funding with a move to the London Stock Exchange’s main market.
This post Bitcoin-Treasury The Smarter Web Company Listed on London Stock Exchange first appeared on Bitcoin Magazine and is written by Micah Zimmerman.
Bitcoin Magazine

Tether Launches Open-Source Bitcoin Mining Operating System
Tether has open-sourced a new operating system for bitcoin mining, unveiling MiningOS (MOS) as part of a broader push to reduce the industry’s reliance on proprietary, vendor-controlled software.
The stablecoin issuer announced Monday that MOS, a modular and scalable operating system designed to manage, monitor, and automate bitcoin mining operations, is now available as open-source software under the Apache 2.0 license.
The system was officially unveiled at the 2026 Plan ₿ Forum in San Salvador.
According to Tether, MOS is built to coordinate the complex mix of hardware, power systems, containers, and physical infrastructure that underpin modern bitcoin mining.
Rather than relying on fragmented software stacks, the operating system treats every component of a mining site as a controllable “worker” within a single operational layer, providing operators with unified visibility across hashrate, energy usage, device health, and site-level infrastructure.
The company said MOS uses a self-hosted, peer-to-peer architecture based on Holepunch protocols, allowing miners to manage operations without relying on centralized services or third-party platforms.
The system is designed to scale from small home installations running on lightweight hardware to industrial-grade deployments managing hundreds of thousands of machines across multiple locations.
“Mining OS is built to make Bitcoin mining infrastructure more open, modular, and accessible,” said Tether CEO Paolo Ardoino. “Whether it’s a small operator running a handful of machines or a full-scale industrial site, the same operating system can scale without reliance on centralized, third-party software.”
Tether’s Mining SDK announcement
Alongside MOS, Tether also announced the Mining SDK, the framework on which the operating system is built. The Mining SDK is expected to be finalized and released in collaboration with the open-source community in the coming months.
The toolkit is designed to allow developers to build mining software and internal tools without recreating device integrations or operational primitives from scratch, offering ready-made workers, APIs, and UI components.
Tether said the goal of open-sourcing its mining stack is to lower barriers to entry for new miners and remove the “black box” nature of many existing mining setups, where hardware and monitoring tools are tightly coupled to proprietary platforms.
The release places Tether alongside other crypto firms pushing open-source mining infrastructure, including Jack Dorsey’s Block, which has previously backed efforts to decentralize mining tooling and hardware access.
MOS marks another step in Tether’s expansion beyond its core stablecoin business. The company has increasingly positioned itself across mining, payments, and infrastructure, reporting more than $10 billion in net profit in 2025, driven largely by interest income on its reserves.
This post Tether Launches Open-Source Bitcoin Mining Operating System first appeared on Bitcoin Magazine and is written by Micah Zimmerman.
CryptoSlate
Ethereum was cheaper than expected in 2020, and rollup decentralization was slower than promised in 2021. Those two realities are forced the ecosystem to rewrite what “a layer-2” is for.
Vitalik Buterin's recent post on Ethereum Research bluntly frames the shift: the original vision of layer-2 (L2) blockchains as “branded shards” of Ethereum is no longer viable, and the ecosystem requires a new path.
However, this isn't abandonment. Instead, it is a re-tiering of expectations and a sharper definition of what different types of rollups are actually building.
The question now is the new job description, since the premise underlying the rollup-centric roadmap has weakened.
Stage 2 is scarce
L2BEAT provides the clearest framework for understanding rollup decentralization through its Stages system.
Stage 0 denotes that training wheels remain in place, with meaningful trust assumptions persisting.
Stage 1 represents partial decentralization with stronger escape hatches and proof guarantees, but still meaningful upgrade or governance trust.
Stage 2 is the “no training wheels” milestone, in which critical safety properties are enforced by code rather than by discretionary actors.
The current distribution of value secured across the L2 ecosystem indicates this. According to L2BEAT's rollup scaling summary, approximately 91.5% of the listed value sits in Stage 1 rollups, 8.5% in Stage 0, and roughly 0.01% in Stage 2.
The top three rollups by value account for roughly 71% of the total, indicating that “Stage 2 progress” largely depends on the decisions of the largest few projects, rather than on what smaller experimental chains attempt.
The core blocker is whether the proof systems can be overridden and whether upgrades face strong delays and constraints.
Upgrade discretion remains common among the largest rollups, and moving beyond it has proven slower and more difficult than anticipated by the 2020-2021 optimism.
Some projects have explicitly stated that they may not wish to proceed beyond Stage 1, citing not only technical constraints related to zkEVM safety but also regulatory requirements that require absolute control.
That's a legitimate product decision for certain customer bases, but it clarifies that those chains are not “scaling Ethereum” in the sense the rollup-centric roadmap originally meant.
| Project | Stage | TVS ($) | Proof type | Upgrade key / security council present? | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Arbitrum One | 1 | 16.16B | Optimistic | Yes | Emergency path can skip delays |
| Base Chain | 1 | 10.99B | Optimistic | Yes | Upgrades approved by multiple parties; no delay |
| OP Mainnet | 1 | 1.88B | Optimistic | Yes | Security council instant upgrade power |
| Lighter | 0 (Appchain) | 1.27B | Validity | Yes | 21d delay, emergency can go to 0 |
| Starknet | 1 | 676.17M | Validity | Yes | Security council can upgrade with no delay |
| Ink | 1 | 523.71M | Optimistic | Yes | Security council + foundation approvals; no regular delay |
| Linea | 0 | 492.93M | Validity | Yes | Multisig can upgrade with no delay |
| ZKsync Era | 0 | 417.07M | Validity | Yes | Emergency board can bypass upgrade delays |
| Katana | 0 | 297.94M | Validity | Yes | security council can remove the upgrade delay |
| Unichain | 1 | 168.81M | Optimistic | Yes | no exit window for regular upgrades; instant powers |
Why the constraints changed
The Oct. 2, 2020, post “A rollup-centric Ethereum roadmap” on the Fellowship of Ethereum Magicians laid out the original thesis.
Gas prices were climbing, some applications were being forced to shut down, and the conclusion was that the ecosystem would be “all-in on rollups” for the near and medium term.
Base-layer scaling should prioritize data capacity for rollups, and users would increasingly live on L2.
Two hard facts have shifted since then. First, L1 is substantially cheaper at present. Etherscan shows a seven-day average transaction fee of around $0.35 and gas snapshots in the fractions of a gwei.
On Jan. 16, Ethereum recorded an all-time high of 2,885,524 transactions in a single day. The narrative is “busier and cheaper,” exactly the opposite of the 2020 crisis that motivated the rollup-centric roadmap.
Second, L1 execution capacity is rising. Ethereum's block gas limit was raised to approximately 60 million after broad validator signaling in late 2025, up from the long-standing 30 million limit.
At roughly 12-second blocks, 60 million gas translates to approximately 5 million gas per second.
Aspirational community discussions have mentioned targets as high as 180 million gas, which would represent a threefold increase, though that remains directional rather than committed.
The clean interpretation: the 2020 premise that “L1 can't scale for most users” is weaker in today's fee regime. This creates room for L2s to be a spectrum of security and sovereignty trade-offs rather than all being near-identical “shards” competing solely on price.

L2s as a spectrum, not clones
Buterin's proposed reframing treats L2s as occupying a full spectrum.
On one end are chains backed by the full faith and credit of Ethereum, with unique properties, not just EVM clones but also privacy-focused systems, non-EVM execution environments, or ultra-low-latency sequencers.
At the other end are options with varying levels of Ethereum connectivity that users and applications can choose based on their specific needs.
The new minimum bar is straightforward: if you handle ETH or Ethereum-issued assets, reach at least Stage 1.
Otherwise, you're a separate L1 with a bridge, and should call yourself that. The differentiation bar is harder: be the best at something other than “cheap EVM.”
Examples Buterin cites include privacy, efficiency specialized to a particular application, truly extreme scaling beyond even an expanded L1, fundamentally different designs for non-financial applications such as social or identity systems, ultra-low-latency sequencing, or features such as built-in oracles or decentralized dispute resolution that aren't computationally verifiable.
The mechanism that might facilitate this is still under investigation. A “native rollup precompile” would enable Ethereum to verify a standard zkEVM proof within the protocol.
For rollups that are “EVM plus extras,” this means the canonical EVM verification occurs trustlessly at the protocol level, and the rollup only needs to prove its custom extensions separately.
This could enable stronger interoperability and pave the way for synchronous composability, in which contracts across different rollups can interact within the same transaction. Yet, it remains a research trajectory, not a deployed feature.
The Jan. 16 post “Combining preconfirmations with based rollups for synchronous composability” and the Feb. 2 post “Synchronous composability between rollups via realtime proving” lay out the design space but don't represent shipped protocol changes.
Three buckets emerging
If this reframing takes hold, expect rollups to split into clearer categories.
The first bucket is Stage 2-chasing settlement rollups that maximize Ethereum security inheritance.
These projects aim to achieve code-enforced guarantees with minimal discretionary governance, treating “scaling Ethereum” as their core mandate.
The second bucket is regulated or controlled execution environments.
These optimize for compliance, permissioning, or specific institutional requirements. They may never progress beyond Stage 1 by design, and they should market that control honestly as a feature rather than pretending to offer full decentralization.
The third bucket is specialized chains optimized for latency, privacy, app-specific execution, or non-financial use cases.
Privacy rollups using zkProofs to hide transaction details, ultra-low-latency sequencers for trading applications, or social and identity systems with fundamentally different state models all fall within this category.
These don't need to be EVM-compatible or even financial to justify their existence, they need to provide value that their users can't get elsewhere.
Projects such as Arbitrum One, Optimism, Base, zkSync Era, and Starknet will each need to decide which category they're pursuing. The ecosystem is large enough to support all three, but the assumption that every L2 performs the same function is fading.

What changes for users and builders
For users, the burden shifts to understanding guarantees. Escape hatches, upgrade delays, proof systems, and censorship resistance become product differentiators rather than assumed properties.
Wallets and interfaces will need to label trust assumptions more explicitly, and the L2BEAT Stages framework aims to make these assumptions legible.
For builders, “cheap EVM” is commoditized. Differentiation moves to privacy and custom virtual machines, ultra-low-latency sequencing, app-specific throughput optimizations, non-financial applications in social, identity, or AI contexts, or compliance and permissioning as an explicit product, without claiming it's “Ethereum scaling.”
For the broader market narrative, expect a louder debate about whether L2s “inherit Ethereum security” in practice rather than as an aspiration.
The critique is already a talking point among rival L1 proponents, and the ecosystem's acknowledgment that many large rollups remain at Stage 1 with discretionary governance gives that critique greater traction.
Is an L2 revolution about to start?
Ethereum is unlikely to see an L2 revolution. Instead, it will witness a re-tiering.
The rollup-centric roadmap assumed that L2s would be near-identical “branded shards” competing primarily on cost, while L1 would remain expensive and capacity-constrained.
That assumption no longer holds. L1 is cheaper and expanding, whereas L2s are diverging faster than they are converging in their security models and use cases, despite Stage 2 decentralization.
The new path acknowledges that reality. L2s that custody ETH or Ethereum-issued assets should meet a minimum security bar, Stage 1 at least. And beyond that, they should compete on specialization and explicit guarantees rather than pretending to be interchangeable.
Native verification primitives and research on synchronous composability signal where Ethereum aims to make that easier, but these are trajectories, not deployed features.
The job description changed.
The minimum bar is to offer credible security when handling Ethereum assets. The differentiation bar is being the best at something, and being honest about the trust model.
The rollup-centric roadmap got upgraded to accommodate the reality that L1 is scaling and L2s are more diverse than the original vision anticipated.
The post Ethereum fees are plummeting so fast that Vitalik Buterin says most Layer 2 chains now lack purpose appeared first on CryptoSlate.
While price action has always been volatile and, arguably, exciting, the Bitcoin network itself is built to feel boring. Ten minutes per block, tick tock, rinse and repeat, a metronome you can set your watch to.
Then every so often, it gets very human again.
Early this morning, block production slowed enough that the average block time briefly spiked to 19.33 minutes. On the surface, it appears to be a technical issue. Below, it reads like a real-time pulse check of an industry that operates on thin margins, loud fans, cheap power, and a lot of stress.

When miners shut down their machines, the network does not immediately adjust. Bitcoin’s difficulty only updates every 2,016 blocks, so if the hashrate drops quickly, blocks come in slower until the next retarget. That gap between reality and the protocol’s response is where you get the weird mornings, the longer waits, the uneasy posts in mining chats, the quiet “something’s off” feeling.
Right now, “off” looks a lot like miners backing away.

The network is telling you miners are stepping back
Over the last stretch of difficulty adjustments, more of them have been negative, and that matters because difficulty is Bitcoin’s way of matching the workload to the number of machines competing to solve blocks.

Hashrate Index’s latest weekly roundup noted the most recent difficulty adjustment on Jan. 22 came in at a -3.28% cut, bringing difficulty to about 141.67T, and it flagged an early estimate for another large negative adjustment in the next cycle, around the Feb. 8 window, with early-epoch projections bouncing near the mid-teens percentage range, while cautioning those estimates can change as the epoch develops.
Other trackers are landing in the same neighborhood. On mempool, the estimated next adjustment is a decline near 15%, and the site’s dashboard has average block time running around the 11 to 12 minute range in the current stretch.
That is slower than the ten-minute target, and it matches the story the charts are trying to tell, miners pulled back, the network is slogging along, the protocol is waiting for the next recalibration.
CoinWarz puts the next difficulty estimate at 121.78T, down about 14.04%, with the average block time around 11.63 minutes, and the retarget date pointing to Feb. 8.

The next adjustment is, therefore, set to be the sharpest drawdown since the post-China-ban era. A block-time spike is a symptom. A run of negative difficulty adjustments is a diagnosis.
Why a 14 to 18% difficulty cut would be a big deal
A double-digit difficulty cut is the protocol admitting the mining economy has changed fast enough that the previous setting no longer fits. For people outside mining, it's background noise. For miners, it is the difference between a fleet that limps along and a fleet that has to shut the lights off.
If the next adjustment lands around 14 to 18%, it would be large enough to put a marker down, especially coming after multiple negative adjustments in recent months. It would also be a reminder that Bitcoin’s difficulty algorithm is a shock absorber, not a crystal ball.
A move that size has happened before, and bigger ones have too.
The largest single downward difficulty adjustment on record came in early July 2021, when difficulty fell about 28% after China’s mining crackdown forced a massive chunk of the global hashrate offline.
So a 14 to 18% cut has precedent, and the network has seen much worse, the context is different though, the China era was a sudden geopolitical shock, today’s pressure looks like a slower squeeze, price, power, and profitability grinding against each other.
The impact for traders is the margin call
Mining is a business where the product is math and the input is electricity, which means the industry lives and dies by spreads.
When Bitcoin’s price falls, miners earn fewer dollars for the same amount of Bitcoin. When power costs rise, or when a region tightens supply during weather events, their input costs climb. When both happen together, older machines and higher-cost sites get pushed out first.
That is why the story keeps snapping back to “who can stay online.”
Hashrate Index’s roundup pegged USD hashprice around $39.22 per PH per day in its snapshot, which is one of the clearest shorthand metrics for miner revenue, and it noted that the forward market was pricing an average hashprice around $39.50 over the next six months.
However, the sharp price drop over the last week has since brought the 6-month forward market pricing down to $32.25.

That little detail is easy to skim past, and it might be the most useful forecasting anchor in the whole dataset. The fact that it repriced lower so quickly suggests the market is settling into a tighter, weaker profitability band rather than betting on a fast recovery.
If you talk to miners when hashprice compresses, the language gets less theoretical. It turns into power contracts, curtailment programs, lenders, machine loans, and the constant question of whether to keep plugging in gear that earns pennies over power, or to shut down and wait for difficulty to come to you.
That is what negative adjustments do, they act like relief.
When difficulty drops, every miner who stays online earns a bit more Bitcoin per unit of hashrate, all else equal. Some of the machines that were pushed out can come back. Some operators get to breathe again.
It is one of Bitcoin’s strange balancing acts, the protocol is indifferent, but the outcome is deeply personal for the people running warehouses of hardware.
What happens next, three paths to watch
The cleanest narrative from here is a difficulty relief bounce.
Difficulty cut
If the network cuts difficulty by something like 14 to 18%, block times should drift back closer to ten minutes, and profitability for online miners improves immediately.
That tends to slow the bleeding, and it can even bring some hashrate back, especially if the underlying issue was marginal economics rather than an external shock. The mempool dashboard on mempool gives a real-time view of whether block times are mean-reverting.
Difficulty cut and price decline
A tougher path is a prolonged squeeze.
Difficulty can fall, and miners can still struggle if Bitcoin’s price keeps sliding, or if energy costs stay elevated, or if credit conditions tighten further for mining firms that rely on financing.
In that world, you can see a loop, hashrate declines, difficulty adjusts down, revenue relief arrives, price pressure returns, and weaker operators get tapped out anyway.
Difficulty cut, price decline, and miner pivot
A third path is quieter, and it is about structural change.
Mining has been drifting toward flexible, power-aware operations for years, the miners that can curtail during peak prices and ramp up when the grid is cheap tend to survive longer.
The industry is leaning harder into that model, along with a shift toward AI. As certain regions face recurring curtailment and more power is diverted to AI, the hashrate line may stay lower for longer, and difficulty adapts to a new equilibrium.
Beyond the immediate operational changes, the shift signals how miners are being forced to adapt to tighter margins, evolving regulatory pressures, and increasing competition for energy resources.
As the industry matures, these adjustments could reshape the balance of power among mining firms, accelerate consolidation, and influence Bitcoin’s long-term network security and decentralization.
What this means for everyone else
For ordinary Bitcoin users, a slower block cadence mostly shows up as waiting, and sometimes as higher fees when demand stacks up. It is not usually catastrophic. It is more like traffic.
For miners, it is the entire business.
For the broader market, it is one of the few times you can see the invisible infrastructure wobble in public, the base layer showing its seams. Bitcoin’s security model is tied to miner revenue in dollar terms, and when that revenue compresses, the conversation about network health gets louder.
The thing is, Bitcoin is designed to keep going through this. Difficulty adjusts. Blocks keep arriving. The metronome finds the beat again.
The interesting part is the story inside that adjustment, the people on the other end of the machines, the operators doing the math at 3 a.m., deciding what stays on and what goes dark, and the network quietly recording those choices in the only language it knows, time between blocks.
If the next retarget lands anywhere near the mid-teens, it will read as a clear signal that miners are stepping back in a meaningful way, and it will also be a reminder that the protocol is still doing what it has always done, absorbing the shock, resetting the difficulty, and letting the system move forward, one block at a time.
The post Bitcoin mining profit crisis hits as difficulty to drop by 14% this weekend while block time spikes to 20 minutes appeared first on CryptoSlate.
US spot Bitcoin exchange-traded funds recorded $561.8 million in net inflows on Feb. 2, ending a four-day streak of nearly $1.5 billion in outflows.
Investors could interpret the number as a return of conviction after punishing outflows, but Jamie Coutts, chief crypto analyst at Real Vision, offered a different read.
According to him:
“Aggregate ETF flows are not buying the dip. Net institutional demand is coming almost entirely from a shrinking group of Treasury-style buyers with remaining balance-sheet capacity. That's not sustainable under continued pressure. A durable Bitcoin bottom likely requires these actors to reverse their positioning — not just slow their selling.”
The distinction matters because ETF inflows measure net share creation in the primary market, not whether the marginal buyer is taking directional Bitcoin risk.
A positive flow print can represent risk-on conviction or risk-off positioning dressed up as demand. The difference hinges on what occurs in the derivatives market immediately after those ETF shares are created.
Flows aren't exposure
Exchange-traded fund creations and redemptions are executed by authorized participants, which are large institutions that keep ETF prices close to net asset value through arbitrage.
When an ETF trades at a premium or discount to its underlying holdings, authorized participants can profit by creating or redeeming shares. That activity shows up as “flows” even when the initiating trade is market structure-driven rather than a macro dip-buy.
More importantly, inflows can represent the spot leg of a delta-neutral basis trade.
Banque de France explicitly describes hedge funds exploiting the futures-spot basis by shorting futures and hedging with long spot exposure via Bitcoin ETF shares.
The central bank notes that basis ranges and annualized equivalents make this trade attractive when volatility and margin costs are stable. CME Group defines basis trading as the simultaneous holding of opposing spot and futures positions to create delta-neutral exposure, with returns arising from basis convergence rather than Bitcoin's price movement.
In practice, this means an institution can buy ETF shares and immediately sell Bitcoin futures or perpetual swaps.
The result resembles institutional demand in headline flow prints, while being economically closer to a carry book than a risk-on bet. The institution earns the spread between spot and futures prices as they converge, clipping an implied yield subject to margin and risk limits.

Five reasons inflows rise without dip buying
Cash-and-carry or basis trades represent the clearest example.
Going long ETF shares while shorting futures or perpetual swaps to achieve basis convergence generates flows that appear bullish, even as net delta exposure remains near zero.
Authorized participant arbitrage adds another layer. Creations and redemptions happen because the ETF traded away from net asset value, not because someone wants Bitcoin exposure.
The flow is the settlement artifact of a pricing discrepancy, not a bet.
Liquidity provision and inventory rebalancing create similar distortions. Market makers may issue shares to meet secondary market demand while hedging elsewhere. The flow appears, but the price support vanishes if the hedge offsets the spot buying.
Cross-venue hedging can directly offset spot buying pressure. Spot purchases to create ETF shares can be matched by futures selling or options hedges, reducing the “price floor” effect even with positive flow prints.
Balance sheet-constrained buyers, who dominate marginal demand, create fragility.
If the primary bid comes from a smaller set of carry players, inflows become episodic and vulnerable to risk-off conditions. This is Coutts' “not sustainable under continued pressure” thesis.
What the positioning data shows
The Commodity Futures Trading Commission's CME Bitcoin futures report shows large gross longs and shorts among non-commercial participants, with sizable spread positions.
That's consistent with systematic relative-value activity being present in the market, exactly what to expect if a meaningful portion of “institutional demand” is hedged rather than directional.
The Banque de France provides basis ranges and annualized equivalents that clarify the economics.
When the expected carry, calculated as futures basis minus financing cost, fees, and margin haircuts, is attractive and volatility remains stable, carry buyers scale the trade and ETF inflows rise.
When volatility spikes or margins increase, or when basis collapses, they de-risk, and flows can flip negative quickly.
This creates a forward-looking distinction. A genuine bottoming process would show basis compressing and futures shorts reducing through covering while ETF inflows persist.
That would signal that inflows are beginning to represent net delta demand rather than just carry.
A fake-out looks different: inflows persist but are matched by rising hedges in futures and perpetual swap markets.
The market gets flow headlines without durable spot support, and any renewed selling pressure forces an unwind.
Coutts' claim suggests the second scenario dominates until proven otherwise.
When inflows actually matter
The clearest test of whether inflows reflect conviction rather than carry is to examine what's happening in derivatives markets.
If ETF inflows are positive while hedges are unwinding, such as basis compresses, futures shorts, and spread positions fall, open interest behavior supports de-risking of carry books, then the inflows likely represent net new demand.
If inflows are positive while futures shorts build or remain elevated, open interest expands in ways consistent with hedging activity, and basis remains wide enough to justify the trade. The flows are plumbing, not positioning.
ETF premiums and discounts to net asset value offer another signal.
When the ETF trades close to NAV, creations are more likely to be mechanical inventory management or basis-trade execution rather than panic bottom-fishing by conviction buyers.
The Feb. 2 inflow of $561.8 million arrived after Bitcoin had already fallen below $73,000. The move pushed Bitcoin to its lowest level since the 2024 election, below its 2024 all-time high of $73,777.
Liquidations had hit $2.56 billion in recent days, according to CoinGlass data. Macro risk-off sentiment, driven by the Kevin Warsh Fed chair nomination and Microsoft's Azure growth disappointment, had soured broader markets.
In that context, a single day of positive flows doesn't prove buyers stepped in with conviction.
It proves that authorized participants created shares. Whether those shares represent directional exposure or the spot leg of a delta-neutral trade determines whether the flows provide price support or merely disguise carry activity as demand.
| If ETF inflows are… | And derivatives look like… | Most likely interpretation | What you’d expect next |
|---|---|---|---|
| Positive | Basis compressing, futures shorts/spread positions fall, OI flat/down, options skew normalizing | Conviction / net delta demand (dip buying) | Better spot follow-through; supports hold |
| Positive | Basis stays wide, futures shorts/spreads rise, OI up, downside hedging persistent | Carry / basis trade (delta-neutral) | Price can stay heavy; flows flip fast if volatility/margins worsen |
| Positive | ETF premium/discount moves trigger creations; derivatives unchanged | AP arbitrage / plumbing | Weak predictive power for direction |
| Negative | Basis collapses + OI falls | De-risking / carry unwind | Volatility spikes; sharper downside possible |
The sustainability question
Coutts' framing of the remaining demand as coming from a shrinking group of Treasury-style buyers with finite balance sheet capacity points to a structural limit.
Basis trades are balance sheet-intensive. Institutions running these strategies face margin requirements, leverage limits, and risk concentrations that constrain how much they can scale.
If the marginal bid comes from this group rather than from conviction-driven allocators, then each incremental dollar of inflow requires more capital and increases fragility.
A durable bottom likely requires a regime shift in which these actors reverse their positioning, not just slow their selling, and in which unhedged directional buyers return in size. Until then, positive flow days can coexist with continued price pressure.
The flows measure plumbing. The price measures whether anyone is actually buying the dip.
The post Bitcoin has ended its $1.5B outflow streak, yet the trade driving inflows could vanish under pressure appeared first on CryptoSlate.
Bitcoin is a $1.5 trillion prize pool secured by nothing more than numbers, private keys, generated by math, that unlock wallets holding real money.
That’s the seductive idea behind Keys.lol: a site that spits out batches of Bitcoin private keys and their corresponding addresses, like an infinite roll of digital lottery tickets.
Refresh the page, and you get another set. Refresh again, and you get another.
Somewhere in that endless stream is a key that matches a wallet with a balance, maybe even one holding a life-changing amount.
This is the only lottery where the game is real, and the jackpot exists, yet the odds are so extreme that “never” is the practical outcome.
The keyspace is so vast that even checking billions of addresses at a time doesn’t meaningfully move the needle; the chance of landing on a funded wallet is so close to zero that it effectively disappears.
Keys.lol feels like a shortcut to fortune, but what it actually demonstrates is the opposite: why Bitcoin wallets are secure, and why brute-force “guessing” isn’t a threat model so much as a lesson in how big numbers can get.
How to play the free Bitcoin lottery
Open the website. Hit refresh. Watch it spit out a new batch of 90 Bitcoin private keys and addresses, like scratchcards scrolling past at high speed.

It feels like a loophole in reality: if you can generate enough keys, fast enough, surely you’ll eventually land on one that already controls real BTC.
That temptation is exactly what Keys.lol is built to dramatize. The homepage claims “every Bitcoin private key” is on the site and encourages you to “try your luck.”
But the punchline is mathematical: yes, you can play, and no, you can’t win, at least not in any practical sense.
I'm not trying to advertise how to “hack Bitcoin.” It’s the opposite: a fun, slightly mind-melting way to understand why Bitcoin wallets are secure.
The space of possible keys and addresses is so large that “randomly guessing” is effectively impossible.
An unintended side effect is that refreshing for long enough may well cure your gambling addiction, too. The fun goes from “but what if I hit one?” to “yeah, this is impossible” pretty quickly.
Keys.lol turns keyspace into a game
Keys.lol doesn’t store a literal database of keys (that would be physically impossible). It generates keys procedurally on the fly based on a page number.
That means it can display deterministic slices of the keyspace without ever saving them.
In other words: it’s not a vault of stolen secrets. It’s a number generator with a balance checker and a casino vibe.
And if you’re refreshing random batches, say 90 addresses at a time, you’re essentially buying free lottery tickets against the entire Bitcoin address universe.
The math behind the impossible odds
A Bitcoin private key is basically a number in an astronomically large range. Keys.lol itself describes it as between 1 and (2^256).
But for this “lottery,” the practical target is addresses with a non-zero balance.
As of February 2026, there are 58 million BTC addresses with a non-zero balance. Let’s use that as the “number of winning tickets.”
Now compare it to the size of the space you’re sampling from.
A standard way to think about Bitcoin addresses is that they’re derived via hashing to a 160-bit value.
- (2^160) possible address-hash outcomes
- That’s about 1.46 × 10^48 possible destinations for “where BTC could be,” in address-space terms
Even if tens of millions are funded, that’s still a rounding error against 10^48.
So what are the odds per refresh?
If you sample addresses uniformly at random from the full space, the probability a single random address is one of the 58,000,000 non-zero ones is:
- p = 58,000,000 / 2^160 ≈ 3.97 × 10^-41
If you check 90 addresses in one go, your chance of finding at least one non-zero balance becomes:
- P(≥ 1) ≈ 90p ≈ 3.57 × 10^-39
That’s roughly:
- 1 in (2.8 × 10^38)
Written out, that’s:
1 in 280,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000 (“280 undecillion.”)
A human way to feel “1 in 2.8×10^38”
Try this mental model:
Imagine you could do one billion refreshes per second (and each refresh checks 90 addresses).
The expected time to hit just one non-zero address would still be on the order of 10^12 years.
The age of the universe is ~10^10 years.
That’s about 10^12 times the age of the universe, or a trillion universe-lifetimes just to find a single funded address.
So you’re not “unlikely” to win. You’re functionally guaranteed not to on any timescale that matters.
How much harder than winning the lottery?
The EuroMillions jackpot odds are about 1 in 139,838,160; the US Powerball odds are 1 in 292,201,338.
Keys.lol's “90-address refresh finds a funded wallet” odds are about 1 in (2.8 × 10^38).
So EuroMillions is roughly:
- (2.8 × 10^38) / (1.398 × 10^8) ≈ 2 × 10^30
That’s about two nonillion times more likely than your refresh ever finding a non-zero address.
Put differently: you’d have a better chance of winning EuroMillions again and again and again than hitting a funded BTC address by random key generation.
This is why Bitcoin wallets are secure
The entire security model of Bitcoin ownership is built on one simple idea:
Even if everyone on Earth used every computer they could possibly build, guessing someone else’s private key is still computationally and probabilistically out of reach.
Keys.lol is compelling because it makes the impossible feel tangible. You’re looking at real-looking keys and real-looking addresses and hoping for a miracle.
But Bitcoin doesn’t rely on secrecy through obscurity. It relies on the sheer scale of the keyspace.
The “attack” you’re simulating, random guessing, isn’t a threat model. It’s a lesson in large numbers.
If you ever “hit” a funded key, it’s theft, not a free jackpot
There’s a reason this “free Bitcoin lottery” is such a useful teaching tool: it exposes the difference between possible in theory and permissible in real life.
If you were to generate a private key that corresponds to a wallet with funds, and then try to “sweep” those coins, you wouldn’t be claiming abandoned treasure.
You’d be taking assets you don’t own, without consent. In plain terms: it’s theft.
Even framing it as “luck” doesn’t change what’s happening. The private key is simply the credential that proves control.
Discovering someone else’s credentials doesn’t grant you ownership any more than finding a stranger’s bank card PIN would.
And there’s a second, subtler risk: trying to turn this into a get-rich scheme can expose you to legal consequences.
Whether it’s prosecuted as theft, fraud, unauthorized access, or another offense depends on the jurisdiction. But the core point is the same: “I guessed it” is not a defense, and “finders keepers” doesn’t apply to digital property.
So yes, Keys.lol is a fascinating window into Bitcoin’s security model. But the only “win condition” here is understanding the math, not trying to cash out someone else’s balance.
“Mathematically never” is still annoying for bots, so Keys.lol adds friction anyway
Even though the odds of finding a funded wallet are so tiny they round to zero for any practical human timeline, Keys.lol still throws up bot protection.
Click “Random page” too aggressively, and you can be redirected to an “Are you human?” captcha.
In other words: even the site itself assumes someone, somewhere, will try to automate refreshes at scale, and it actively tries to slow that down.
That doesn’t make Bitcoin “more secure” (the security comes from the size of the keyspace). But it does make this particular game harder to industrialize.
It’s a reminder that brute-force behavior is expected, and throttled, even when the underlying math already makes success effectively impossible.
The “expected reward” of a refresh (and why the fun math is misleading)
Let’s do some back-of-the-napkin maths anyway.
The average non-zero wallet holds about 0.126 BTC, and we can value that at roughly $9,852 today, then the arithmetic is:
- $9,852 ÷ 58,000,000 ≈ $0.0001362069
- That’s about $1 per 9,852 in this simplified framing.
But here’s the catch: that calculation quietly assumes each refresh is picking from the set of funded wallets.
In reality, you’re sampling from the full address universe. The microscopic part is the chance of landing on any of those 58 million non-zero addresses at all.
Once you include that probability, the true expected value collapses to essentially zero.
Using today’s BTC price (~$78,195), 0.126 BTC is about $9,852.
But the expected value per 90-address refresh is still only about:
- $3.5 × 10^-35 per refresh
That’s the kind of number where “expected $1” would require roughly 2.8 × 10^34 refreshes on average.
Bitcoin’s market cap is currently around $1.5T on major trackers (it fluctuates daily).
That headline number is what makes the “free lottery” feel so seductive: a giant pool of value, sitting behind “just a number.”
But the lock is better than anything physical, it is built on cold, hard math.
Play the lottery on the first page of Bitcoin private and public keys.
The post The trillion dollar Bitcoin lottery you can play now for free – but will never win appeared first on CryptoSlate.
Bitcoin fell around 8% on Feb. 3, briefly losing the $73,000 level.
A quick rebound took prices to $74,500 as of press time, dampening the intraday correction to 5.8%. The decline marks the lowest price point in the President Donald Trump administration and the weakest level since the November 2024 Presidential Election.
The selloff pushed Bitcoin as low as its March 2024 all-time high of $73,500, a level that held through the early stages of the decline but ultimately gave way under sustained selling pressure.
The move revived a cluster of support zones that traders have monitored as critical technical thresholds for nearly a year.
Macro risk-off drives crypto lower
The crypto weakness is linked to broad risk-off sentiment across markets, sparked by Trump's nomination of Kevin Warsh as Federal Reserve chair.
Warsh's selection stoked concerns about a more hawkish policy mix and tighter financial conditions, pressures that historically weigh on high-beta assets, including cryptocurrencies. A stronger dollar, which typically accompanies such expectations, compounds the headwind for digital assets. The current dollar weakness, however, makes this decline even more painful.
Microsoft's Azure growth disappointment added to the selling pressure, souring broader risk sentiment and triggering cross-asset contagion.
The AI trade wobble demonstrated how crypto remains vulnerable to spillover effects from growth-sensitive technology sectors, particularly when positioning is stretched and liquidity is thin.

Leverage unwind amplifies decline
CoinGlass data shows over $2.5 billion in Bitcoin liquidations in recent days, turning what began as a macro-driven selloff into a cascade of forced selling.
Thin weekend liquidity exacerbated the selloff that began at $84,000 on Saturday, according to a Bitfinex note.
The combination of macro triggers and leverage unwinding created conditions in which relatively modest initial selling pressure could force far larger moves, as stop-losses and margin calls compounded the decline.
Additionally, institutional flows in 2026 have been uneven.
Exchange-traded fund (ETF) inflows, often followed by outflows during volatility episodes, suggest tactical rebalancing rather than aggressive dip-buying, leaving prices exposed as liquidation pressure accelerates.

The absence of consistent institutional demand meant there was no meaningful buffer when forced selling began.
Galaxy Digital research also noted that near-term catalysts appear scarce, with diminished odds of legislative progress on market structure acting as a narrative headwind.
Without clear positive drivers on the horizon, traders lack the conviction to step in aggressively during drawdowns.
Critical support and resistance levels
Bitcoin now trades within a tightly watched technical range.
The $73,500 level from 2024 and the Feb. 3 intraday low of $72,945 form the immediate support zone.
IG Markets identifies a broader support band between $73,581 and $76,703, an area associated with prior cycle highs and 2025 lows that has been tested multiple times over the past year.
CryptoSlate also identified several support and resistance levels for 2026 in Akiba's bear market analysis.
A daily close below this band would increase the probability of follow-through selling toward the next support cluster between $72,757 and $71,725. If that zone fails to hold, the July 2024 peak of around $70,041 becomes the next major downside waypoint.
On the resistance side, Bitcoin's reclamation of the 2024 all-time high of $73,500 indicates that buyers are willing to defend the recent breakdown level. The April 2025 trough zone around $74,508 now acts as resistance after previously serving as support.
Above that, minor resistance sits at $78,300, with the November 2025 low of $80,620 and the psychological $80,000 level forming the next meaningful barrier.
Distinguishing bounce from recovery
A single-day rebound does not constitute a durable bottom.
Historical patterns suggest that sustainable recoveries typically require at least two conditions: repeated daily closes above the $74,500 level, converting the April 2025 reference zone from resistance to support, and evidence that liquidation pressure has faded following the $2.56 billion forced-selling wave.
Without these confirmations, rallies risk becoming dead-cat bounces into overhead resistance as sellers use strength to exit positions.
ETF flows must stabilize beyond isolated green days, consistent with the tactical rather than aggressive institutional behavior.
Two near-term scenarios
If Bitcoin holds the $73,000 to $73,445 support zone and reclaims $74,500, the path of least resistance becomes a grind toward $78,300, then the $80,000 to $80,620 range.
This scenario requires both technical follow-through and the absence of new macroeconomic headwinds.
Alternatively, a daily close below the $73,581 lower band increases the odds of continuation selling into the $72,757 to $71,725 zone, with the $70,000 level as the next major psychological and technical waypoint.
This scenario becomes more likely if liquidation pressure remains elevated or if macro conditions deteriorate further.
Bitcoin's decline below its 2024 all-time high after nearly a year of holding that level as support constitutes a technical breakdown, shifting the burden of proof to buyers.
The combination of macro risk-off sentiment, leverage unwinding, and tactical institutional flows created conditions in which support levels that had held for months gave way within hours.
The post Bitcoin in freefall hitting lowest price since Trump took office as leverage turns a macro wobble into a brutal cascade appeared first on CryptoSlate.
HTTP error 429 on https://cryptoticker.io/en/feed/
Failed to fetch feed: https://cryptoticker.io/en/feed/
Failed to fetch feed.
Decrypt
Investor pushback on a $500 billion valuation has reportedly prompted Tether to rethink the size of its planned capital raise.
The Ethereum co-founder says that prediction markets and creator DAOs would reward inherent value, rather than celebrity or virality.
World Liberty Financial's $500 million deal with the UAE is causing major backlash in Congress, with the Clarity Act caught in the crossfire.
Prediction market users increasingly think that Strategy will sell some BTC—but analysts don't think Bitcoin's price crash "changes anything."
Crypto.com’s standalone platform OG arrives as multiple states are taking enforcement actions against prediction market operators.
U.Today - IT, AI and Fintech Daily News for You Today
Dogecoin sees substantially low performance among futures traders over the last day as only $1.16 billion worth of DOGE tokens were committed in active contracts.
Solana price is hanging in the balance as on-chain data show that a possible rebound is imminent.
Surge in derivatives activity follows as the broader crypto market experienced a sell-off.
Shiba Inu is surging in future market flows, which might not translate to price performance as swiftly as you would expect.
Wednesday, Feb. 4: DOGE jumps on Musk's $850 billion record as ETH tests a 24% rally setup. Cardano (ADA) flips BCH in a high-volume midweek market shift. Read more.
Blockonomi
TLDR
- Tesla stock was flat at $421.80 on Wednesday as investors awaited developments on the Optimus humanoid robot with production planned for 2026.
- An X poll showed Optimus winning as investors’ most anticipated Tesla product for the year, beating Cybercab and semi-truck options.
- Tesla is converting its Fremont Model S and Model X production space into an Optimus factory targeting one million units annually.
- The company will discontinue the Model S and Model X to make room for Optimus production lines at the California facility.
- Tesla stock trades at 259 times earnings with a $1.4 trillion market cap as the company transitions from electric vehicles to AI robotics.
Tesla stock held steady at $421.80 on Wednesday morning. The lack of movement came as investors digested recent developments around the company’s humanoid robot project.
Tesla, Inc., TSLA
S&P 500 and Dow futures traded higher by 0.3% and 0.2% respectively. No analyst rating changes or price target adjustments hit the stock during the session.
The most interesting development came from social media. A poll on X asked investors which Tesla product excited them most for the year ahead.
Optimus won by a landslide. The humanoid robot beat out the Cybercab, semi-truck, and stationary storage in voting. Over 16,000 votes were tallied by early Wednesday.
The poll reflects growing anticipation around Tesla’s robotics push. CEO Elon Musk has repeatedly called Optimus the company’s future.
A Factory Transformation Underway
Musk outlined specific plans during Tesla’s January 28 earnings call. The company will convert Model S and Model X production space at its Fremont, California factory.
That space will become an Optimus manufacturing facility. The long-term target is one million robot units per year from that location alone.
Production should begin in 2026. Musk said Tesla plans to unveil the third generation robot in “a few months.”
The decision to retire legacy vehicle models shows serious commitment. Model S and Model X currently represent a small portion of Tesla’s sales. But discontinuing them marks a clear pivot point for the company.
Tesla is moving resources from traditional electric vehicles to AI-powered products. This includes both Optimus and the Robotaxi ride-hailing service.
The Numbers Tell a Stretched Story
Tesla’s market cap sits at $1.4 trillion. The stock trades at $430 per share based on recent pricing.
The company finished its 2025 fiscal year with non-GAAP earnings of $1.66 per share. That puts the stock at 259 times earnings.
Analysts project earnings of $2.12 per share for 2026. They forecast $3.00 per share by 2027. Even using those future estimates, Tesla trades above 100 times earnings two years out.
Tesla stock has gained 10% over the past 12 months. But it dropped about 2% following the January earnings report.
The earnings call generated one downgrade from Battleroad Research analyst Ben Rose. He cited higher capital spending on AI projects as a concern.
Tesla plans to spend $20 billion on new plants and equipment in 2026. That’s up from less than $9 billion in 2025.
The average analyst price target rose by about $4 after earnings. That increase represents less than 1% movement.
Experts believe the humanoid robotics market could reach $5 trillion by 2050. Musk wants Tesla positioned as an early mover in that space.
Other companies are already training humanoid robots for factory work. Some industry watchers speculate Optimus could perform real-world applications later in 2026.
Tesla’s vehicle business has declined as the company shifts focus. Musk appears comfortable with this transition.
The stock reflects a loyal shareholder base willing to wait for long-term potential. Whether current prices leave room for near-term gains remains unclear.
Tesla plans to unveil the third generation Optimus robot in the coming months.
The post Is Tesla (TSLA) Stock a Buy as Optimus Robot Production Nears? appeared first on Blockonomi.
TLDR
- AbbVie reported Q4 adjusted earnings of $2.71 per share, beating analyst expectations of $2.65
- Revenue reached $16.6 billion in the quarter, surpassing the $16.4 billion estimate
- 2026 adjusted earnings guidance of $14.37 to $14.57 per share tops consensus view of $14.27
- Oncology revenue dropped 2.5% and aesthetics revenue fell 1.2% on an operational basis
- Humira sales plunged 26% to $1.2 billion as biosimilar competition intensifies after 2023 patent loss
AbbVie shares dropped 3.6% on Wednesday despite the drugmaker posting solid quarterly results and upbeat guidance for the year ahead. The stock’s decline came even as the company topped Wall Street estimates across key metrics.
The pharmaceutical company reported adjusted earnings of $2.71 per share for the fourth quarter. That beat analyst expectations of $2.65 per share. Revenue came in at $16.6 billion, topping the $16.4 billion consensus estimate.
AbbVie Inc., ABBV
For 2026, AbbVie issued guidance that exceeded market expectations. The company expects adjusted earnings between $14.37 and $14.57 per share. Analysts had predicted $14.27 per share.
But investors focused on weakness in certain business segments. Oncology revenue hit $1.7 billion in the quarter, down 2.5% on an operational basis. The aesthetics portfolio, which includes Botox Cosmetic and Juvederm, generated $1.3 billion in revenue, falling 1.2% operationally.
Immunology Growth Led by Skyrizi and Rinvoq
The immunology portfolio delivered strong performance with $8.6 billion in revenue, up more than 18% from the prior year. Skyrizi recorded sales of $5.01 billion, growing 32.5% and beating estimates of $4.82 billion. Rinvoq sales grew 29.5% to $2.37 billion, though slightly missing estimates of $2.41 billion.
These newer immunology drugs are filling the gap left by Humira. The once-blockbuster drug saw revenue fall 26% to $1.2 billion in the quarter. However, this figure surprisingly beat analyst estimates of $983.8 million, marking the first time in nearly two years that Humira sales exceeded expectations.
Humira lost market exclusivity in 2023. The drug now faces fierce competition from biosimilars, which are near copies of biological drugs sold at lower prices. At its peak in 2022, Humira generated more than $21 billion in global sales.
Botox Cosmetic Shows First Growth Since Q3 2024
The aesthetics business showed signs of life. Botox Cosmetic sales reached $717 million, beating estimates of $696.2 million. This marked the first revenue growth since the third quarter of 2024.
Demand for the anti-wrinkle injection has been pressured by customer concerns about the economy and inflation. New competition from companies like Revance and Evolus has also eaten into market share.
AbbVie has been actively investing to drive future growth. The company has spent more than $20 billion on acquisitions recently. It plans to invest another $10 billion over the next decade, including building four new manufacturing plants in the United States.
The stock’s weakness came even as the broader market edged higher. Futures tracking the S&P 500 rose 0.1% in morning trading. Fellow drugmaker Eli Lilly gained 9% after reporting its own strong earnings results.
Shares briefly rose in premarket trading before reversing course. The decline suggests investors remain concerned about revenue pressures in oncology and aesthetics despite the company’s overall financial strength.
AbbVie’s Q4 adjusted earnings of $2.71 per share and revenue of $16.6 billion both exceeded Wall Street expectations, while 2026 guidance of $14.37 to $14.57 per share topped the $14.27 consensus estimate.
The post AbbVie (ABBV) Stock: Why Shares Are Falling Despite Earnings Beat and Strong 2026 Guidance appeared first on Blockonomi.
TLDR
- BTIG upgraded Cloudflare stock from Neutral to Buy with a $199 price target, sending shares up 2.2%
- Field checks with five partners representing over $100M in annual sales showed strong momentum across multiple business segments
- Analyst believes Cloudflare can maintain high 20s revenue growth through 2028
- Stock has dropped 33% since November 2025 but analyst sees the pullback as a compelling entry point
- Fourth quarter earnings scheduled for February 10, 2026
Cloudflare stock jumped 2.2% Wednesday after receiving an upgrade from BTIG analyst Gray Powell. The analyst raised his rating from Neutral to Buy and set a price target of $199.
Cloudflare, Inc., NET
Powell’s upgrade followed extensive research with Cloudflare partners. He spoke with five partners who collectively handle over $100 million in annual Cloudflare sales. The feedback was uniformly positive across the company’s business lines.
The analyst highlighted three key growth areas for the cloud services provider. Web application protection remains a core strength that markets may be undervaluing. Zero Trust and SASE segments are seeing rapid share gains. Developer services have built clear momentum throughout 2025 and into 2026.
Growth Trajectory Remains Strong
Powell projects Cloudflare can sustain revenue growth in the high 20s through 2028. This forecast comes from detailed product-level analysis. The analyst expressed confidence in the company’s upcoming earnings report.
Cloudflare will report fourth quarter results on February 10, 2026. The timing of the upgrade suggests BTIG expects solid numbers.
The stock has faced headwinds in recent months. Shares have fallen 33% since early November 2025. This decline exceeded both the broader software sector’s 26% drop and BTIG’s security coverage universe’s 22% decline.
Valuation Debate Continues
The company trades at 18.8x CY27E EV/sales. High-growth peers trade at 9.1x by comparison. The valuation gap is substantial.
Powell acknowledges the premium pricing remains a concern. However, he views the recent selloff as creating an attractive entry point. He called it “a compelling entry point into the top growth story” within BTIG’s coverage.
The analyst sees potential AI-related tailwinds for Cloudflare. This contrasts with broader market worries about AI’s impact on software business models. Many investors fear AI could disrupt traditional software economics.
Powell’s channel checks revealed consistent strength across Cloudflare’s portfolio. Partners reported strong demand for core products. The Zero Trust and SASE categories showed particular strength.
Web application protection continues to drive the business. The analyst believes this market opportunity gets insufficient credit. Growth in this segment appears sustainable based on partner feedback.
Developer services represent an emerging growth driver. Momentum in this area has accelerated over recent quarters. Partners indicated increasing customer interest in these offerings.
The upgrade comes as software stocks face pressure from multiple angles. Valuation concerns and AI disruption fears have weighed on the sector. Cloudflare has not been immune to these trends.
The 33% decline since November created the opening Powell needed to upgrade. At current levels, the risk-reward profile looks more attractive. The $199 price target implies roughly 25% upside from pre-upgrade levels.
Partner conversations spanning over $100 million in sales provided conviction for the call. This sample size offers meaningful insight into Cloudflare’s business trajectory. The consistency of positive feedback across multiple partners strengthened the case.
BTIG’s upgrade reflects confidence in Cloudflare’s competitive position. The analyst sees the company taking share in key markets. Product momentum appears to be building rather than fading.
The February 10 earnings report will provide the next major catalyst. Investors will look for confirmation of the trends Powell identified in his research.
The post Cloudflare (NET) Stock: Analyst Upgrade Sends Shares Higher on Growth Optimism appeared first on Blockonomi.
TLDR
- Boston Scientific reported Q4 adjusted earnings of 80 cents per share, beating analyst estimates of 78 cents
- Net sales reached $5.29 billion with 12.7% organic growth, slightly above Wall Street expectations
- Q1 guidance disappointed with projected growth of 8.5% to 10% versus analyst expectations of 9.8%
- Electrophysiology division underperformed with $890 million in sales versus consensus expectations of $933 million
- Stock dropped 8.4% in premarket trading despite the earnings beat
Boston Scientific shares took a beating Wednesday morning despite posting better-than-expected fourth-quarter results. The culprit? Weak guidance for the current quarter and disappointing performance in a key division.
The medical device maker reported adjusted earnings of 80 cents per share for the fourth quarter. That topped the Street’s call for 78 cents. Net sales came in at $5.29 billion, representing 12.7% organic growth year-over-year and edging out the $5.28 billion analysts were expecting.
Boston Scientific Corporation, BSX
So why the selloff? The first-quarter outlook fell short of expectations.
Boston Scientific projects organic growth of 8.5% to 10% for the current quarter. Analysts had penciled in 9.8% growth. The company also forecast adjusted earnings of 78 cents to 80 cents per share for Q1, at the low end of what Wall Street wanted to see.
Shares plunged 8.4% in premarket trading following the announcement. The stock had already declined 8.7% since being featured as a Barron’s stock pick in October.
Electrophysiology Division Falls Short
The weakness wasn’t uniform across all business segments. The electrophysiology division, which accounts for roughly 17% of fourth-quarter revenues, missed expectations by a wide margin.
The division posted sales of $890 million. That came in well below the consensus estimate of $933 million and Stifel’s projection of $903 million. The shortfall appears concentrated in the U.S. market, raising questions about demand trends.
Electrophysiology is a closely watched segment for Boston Scientific. The miss there likely contributed to investor concerns about near-term momentum.
The earnings beat itself came with an asterisk. Boston Scientific benefited from a lower-than-expected tax rate of approximately 9.3%. Stifel had modeled a rate of 13.5%, meaning the bottom-line beat was more about tax benefits than operational outperformance.
Full-Year Outlook Meets Expectations
The picture looks brighter when zooming out to the full year. Boston Scientific guided to adjusted earnings of $3.43 to $3.49 per share for 2026. The company expects organic growth of 10% to 11% for the year.
Both ranges align with consensus estimates. The guidance suggests Boston Scientific expects growth to accelerate in the second half of the year, given the slower start projected for Q1.
Organic revenue growth reached 15.9% in the fourth quarter, surpassing Stifel’s projection of 15%. That strong finish to 2025 makes the Q1 guidance look more conservative by comparison.
Total fourth-quarter revenue of $5.29 billion beat Stifel’s estimate of $5.25 billion. The company demonstrated solid performance across most of its portfolio, with the electrophysiology division being the main exception.
The tax rate for the quarter came in at 9.3%, well below typical levels and analyst expectations. That tailwind boosted earnings but may not be sustainable in future quarters.
Boston Scientific’s Q1 organic growth guidance of 8.5% to 10% implies a deceleration from the 15.9% pace in Q4. The company appears to be building in conservatism or facing tougher comparisons in the near term.
The electrophysiology division’s U.S. weakness particularly stands out given the segment’s importance to the overall growth story. Investors will be watching closely to see if this represents a temporary blip or a more sustained trend.
The post Boston Scientific (BSX) Stock: Why Shares Drop 8% Despite Earnings Beat appeared first on Blockonomi.
TLDR
- Uber reported Q4 adjusted earnings of 71 cents per share, missing Wall Street estimates of 85 cents
- Revenue increased 19% to $14.4 billion, beating forecasts of $14.3 billion
- Q1 earnings guidance of 65-72 cents per share falls below analyst expectations of 81 cents
- Uber expanding robotaxi services to Hong Kong, Madrid, Houston, and Zurich
- Stock dropped 8.5% to $71.32, down 22% from October record high of $100.10
Uber Technologies reported fourth-quarter earnings that disappointed investors despite strong revenue growth. The ride-hailing company posted adjusted earnings of 71 cents per share, falling well short of the 85-cent consensus estimate from analysts.
Shares tumbled 8.5% to $71.32 on Wednesday following the announcement. The stock has now declined 22% from its record closing high of $100.10 reached on October 6.
Uber Technologies, Inc., UBER
Revenue told a different story. Uber brought in $14.4 billion for the quarter, up 19% from last year on a constant currency basis. That figure topped Wall Street’s projection of $14.3 billion.
The earnings miss came down to pricing strategy. Uber lowered prices to boost trip volume, which squeezed profit margins. The approach worked for growth, with total trips jumping 22% during the quarter.
Gross bookings reached $54.1 billion in the fourth quarter, up 22% year-over-year. This marked the third consecutive quarter where Uber exceeded bookings expectations but missed on operating income forecasts.
Weak Guidance Pressures Stock
The first-quarter outlook added to investor concerns. Uber projected adjusted earnings between 65 cents and 72 cents per share, below the 81-cent analyst consensus.
The company expects gross bookings of $52 billion to $53.5 billion for the current quarter. That range sits above Wall Street’s estimate of $51.4 billion.
Robotaxi Expansion Accelerates
Uber announced plans to launch driverless rides in four new cities during its earnings presentation. Hong Kong, Madrid, Houston, and Zurich will soon offer autonomous vehicle services through the platform.
The Hong Kong launch represents Uber’s first robotaxi entry into the Asian market. The company plans to partner with Baidu, which already holds licenses for driverless trials in the city.
For Zurich, Uber will likely work with WeRide, a company that has secured autonomous driving permits in Switzerland. This partnership approach keeps costs down while allowing rapid expansion.
Uber aims to operate autonomous vehicles in more than 10 global markets by the end of 2026. The company didn’t provide specific launch dates but confirmed partnerships with previously announced technology providers.
These partners include Lucid Group for the San Francisco Bay Area and Volkswagen for Los Angeles. Uber positions itself as the platform connecting various autonomous vehicle providers to customers.
The asset-light strategy avoids the massive capital requirements of building and maintaining a proprietary fleet. Instead, Uber leverages existing technology partners to scale quickly.
Analysts maintain a positive outlook on the stock despite the earnings miss. The consensus rating stands at Strong Buy based on 28 Buy ratings, three Hold ratings, and one Sell rating.
The average 12-month price target of $112.31 suggests 44% upside potential from current levels. Over the past year, the stock has gained 11.7%.
Shares hit their lowest level since April 2025 in Tuesday’s trading session before the earnings release. The stock remains down 22% from its October peak as investors weigh growth investments against near-term profitability.
The post Uber Stock Slides After Earnings Miss Despite Revenue Growth appeared first on Blockonomi.
CryptoPotato
Hyperliquid seems to be the talk of the town lately, and Ripple just announced that its Ripple Prime brokerage platform will support Hyperliquid. In other words, the firm’s institutional clients will be able to access on-chain derivatives while cross-margining their exposure to decentralized finance with all other assets that are supported by Ripple Prime.
These include cleared derivatives, OTC swaps, fixed income, forex, and other digital assets.
According to the official release, “clients can access Hyperliquid liquidity while benefiting from a single counterparty relationship.”
Speaking on the matter was Michael Higgins, the international CEO of Ripple Primer, who said:
“At Ripple Prime, we are excited to continue leading the way in merging decentralized finance with traditional prime brokerage services, offering direct support to trading, yield generation, and a wider range of digital assets. This strategic extension of our prime brokerage platform into DeFi will enhance our clients’ access to liquidity, providing the greater efficiency and innovation that our institutional clients demand.”
Ripple continues to expand its product offering while also working on licensing and regulatory issues worldwide. Recently, they secured a preliminary electronic money institution license in Luxembourg.
The move to integrate Hyperliquid into their prime brokerage solution also comes at a time when the decentralized perpetual futures exchange is attracting billions in daily volumes across a variety of assets, providing the deepest on-chain liquidity order book in the industry.
The post Ripple Announces Institutional Support for Hyperliquid appeared first on CryptoPotato.
Ethereum has extended its corrective phase and is now trading at a technically decisive area, where higher-timeframe demand and market structure intersect. The price behaviour around this zone is critical in determining whether ETH stabilizes in a broader range or resumes its downside momentum.
Ethereum Price Analysis: The Daily Chart
On the daily timeframe, Ethereum has reached a crucial support zone around the $2K area, which aligns with a major prior yearly low and a historically significant demand region. This level has previously acted as a strong base for accumulation, and the market’s reaction here suggests growing sensitivity among participants.
The sharp sell-off into this zone reflects aggressive bearish momentum, but the absence of immediate continuation lower indicates that selling pressure may be temporarily exhausting. From a structural perspective, this area represents a decision point where sustained acceptance below it could open the door to deeper downside, while stabilization above it increases the probability of consolidation.
At this stage, the most likely outcome on the daily chart is a consolidation and range-bound phase as the market digests recent losses and awaits fresh demand or a clear macro catalyst.
ETH/USDT 4-Hour Chart
On the 4-hour timeframe, the price action shows a descending fluctuation while holding within the critical $2K support range. The market is compressing after the impulsive sell-off, with lower highs forming against relatively stable lows, a behaviour often seen near short-term exhaustion points.
This structure leaves room for a temporary bullish rebound, driven by short-covering or reactive demand, particularly after the steep downside move. However, this potential rebound should be viewed as corrective rather than trend-reversing.
The dominant scenario remains an expanded range environment, where Ethereum oscillates within a defined structure, bounded by $2K and $3K threhsolds, until meaningful demand enters the market or a new supply zone forms above, reasserting directional bias.

Sentiment Analysis
The Ethereum Coinbase Premium Index is currently deeply negative and has dropped to levels last seen around the previous year’s major market lows, signalling a clear bearish state in market sentiment. This persistent negative premium reflects sustained selling pressure from US-based investors, with Ethereum trading at a discount on Coinbase relative to offshore exchanges.
Historically, such conditions indicate weak spot demand from institutional and high-conviction buyers, reinforcing the broader corrective structure seen on price charts.
However, it is also important to note that in past cycles, Ethereum has consistently shifted into a bullish phase only after this indicator recovered and turned positive, signalling the return of strong spot demand. As long as the premium remains negative, downside risk and range continuation dominate, leaving the market in a bearish state.

The post Ethereum Price Prediction: Will ETH Inevitably Drop Below $2K This Month? appeared first on CryptoPotato.
Bitcoin’s (BTC) slide below $80,000 has intensified worries that a wider downturn in the broader crypto sector could be imminent.
Market experts believe that the recent slide in BTC’s price may not be an isolated correction, but a development that could seriously destabilize corporate balance sheets and magnify systemic risk if it continues to fall.
Major Market Casualty
Michael Burry has issued a stark warning that Bitcoin’s continued decline could erase significant value across the market, and the greatest risk is concentrated among companies that have built large corporate treasuries around the asset, which have mushroomed over the years.
In the latest Substack post following the latest crypto sell-off, “The Big Short” investor, Burry, said BTC’s drop below important technical levels opens the door to cascading stress not only within crypto markets but also across adjacent financial sectors.
He said that the world’s largest crypto asset is failing to meet a critical expectation often placed on it, that is, acting as a hedge against currency debasement. Instead, Burry said its recent behavior more closely resembles that of a speculative risk asset, particularly given its correlation with the S&P 500. He said gold and silver rallied on geopolitical uncertainty and dollar weakness, but Bitcoin did not follow those macro signals.
Burry also predicted that further downside could have severe consequences for Bitcoin treasury companies that accumulated BTC aggressively during higher price ranges. He highlighted the possibility that another 10% decline could leave major holders such as Michael Saylor’s Strategy billions of dollars underwater, and potentially cut them off from capital markets, thereby increasing bankruptcy risk.
Such outcomes, according to the investor, could amplify losses beyond individual firms and contribute to broader market fallout. Burry additionally noted that Bitcoin’s weakness has coincided with recent pressure in precious metals.
Galaxy Digital’s Zac Prince also questioned the long-term viability of Bitcoin treasury companies, which raise capital to hold BTC on their balance sheets while promising yield. Speaking on TheStreet Roundtable, Prince said these models rely on risky financial engineering rather than BTC’s native value. He compared them to past schemes that created tokens to generate Bitcoin and said that paying a premium for such structures does not make them sustainable.
He even explained that while some firms might pivot to revenue-generating activities, many will still struggle to justify their valuations, and added that businesses should focus on real operations first and treat BTC as a treasury strategy, not the primary driver.
Optimism Wanes
Bitcoin has been under tremendous pressure, and many analysts believe that there could be more pain ahead instead of a much-anticipated recovery.
Former Binance CEO Changpeng “CZ” Zhao also said that while he had been positive about a BTC super cycle just weeks ago, current market sentiment has made him less confident. Speaking on Binance’s social platform, he highlighted the rise of fear, uncertainty, and doubt (FUD) in the community and admitted that the emotional intensity has left him uncertain about BTC’s near-term prospects.
The post Michael Burry Warns Bitcoin Treasury Firms Face Existential Risk as BTC Slide Deepens appeared first on CryptoPotato.
The largest altcoin was hit hard over the past few weeks, dropping from over $3,000 to a multi-month low of $2,100.
Despite this substantial double-digit crash in the span of mere days, though, a few popular analysts recently indicated that the bottom has not been reached yet.
One of them, going by the X handle CW, indicated that ETH plummeted to a major buying wall at $2,100. If it’s to reverse anytime soon, the first significant sell wall is at $2,560.
Ali Martinez based his bottom prediction on the Market Value to Realized Value (MVRV) band, a metric that helps identify potential trend reversals.
He said that Ethereum has historically bottomed out when it dropped below the 0.80 MVRV band. If history repeats itself now, it would result in a price drop to just under $2,000.
Ethereum $ETH bottoms have historically formed below the 0.80 MVRV band.
Today, that level is near $1,959. pic.twitter.com/cgcuy2OgvI
— Ali Charts (@alicharts) February 4, 2026
Crypto Tony shared a similar opinion. The analyst with over 560,000 followers on X noted that ETH could go down to the major support and psychological level of $2,000 before it rebounds decisively.
His chart is quite optimistic as it shows a quick surge to $3,600 before another calamity to yearly lows at $1,500 by the summer of 2026. However, the 1-week macro chart is highly bullish as it predicts a massive run to new all-time highs above $6,000.
$ETH / $USD – Macro Update
Personally i am looking for a bottoming to come in at $2000 level. Major support zone and a psychological level. pic.twitter.com/8VGHOQOx9t
— Crypto Tony (@CryptoTony__) February 4, 2026
The post ETH Dumps 25% in a Week, but Analysts Say the Bottom Isn’t In Yet appeared first on CryptoPotato.
Bitcoin (BTC) slid to around $72,800 yesterday as U.S. lawmakers debated a stopgap funding package before rebounding once the House passed the bill on February 4, 2026, easing fears of a government shutdown.
The quick turnaround showed how closely crypto prices still track U.S. political risk, even when no blockchain-specific news is involved.
Shutdown Fears Ripple Through Crypto
According to a February 4 post by on-chain analytics firm Santiment, the sell-off unfolded during U.S. trading hours while headlines pointed to a tight vote in the House. As uncertainty built, BTC quickly fell, triggering about $30 million in DeFi liquidations and mirroring a synchronized drop in the S&P 500 and even gold, an asset typically viewed as a safe haven.
This correlation indicates traders were reducing exposure to volatile assets broadly due to the political standoff, not crypto-specific news.
The concern centered on whether Congress would approve a roughly $1.2 trillion funding package to keep most federal agencies running through September 30. Failure would have led to a partial shutdown, delaying economic data and adding stress to an already cautious market.
The tense vote saw Republican divisions, with one representative voting against the bill due to foreign aid provisions.
However, the bill ultimately passed, averting a shutdown and causing markets to respond with immediate relief. Bitcoin bounced from its lows, climbing over 5% within hours, and the S&P 500 also recovered. According to Santiment, the speedy recovery showed that fears of political dysfunction, rather than a fundamental reevaluation of Bitcoin’s value, were behind the earlier sell-off.
Broader Pressures on Bitcoin’s Price
While the funding bill news provided a clear short-term catalyst, Bitcoin is still facing broader headwinds. Per data from CoinGecko, the asset is down nearly 14% in the last seven days and 17% for the month.
A recently published analysis from Galaxy Digital pointed to deteriorating on-chain metrics, with research head Alex Thorn noting that 46% of Bitcoin’s circulating supply is now “underwater,” meaning it was last moved at higher prices, which can increase selling pressure. He also pointed out that there was a lack of significant accumulation by large holders.
Furthermore, on February 3, reports that Iran was seeking to shift the format of nuclear talks with the U.S. contributed to another leg down in Bitcoin’s price, pushing it below $75,000 and burning at least $20 million worth of derivative positions.
Additionally, some analysts like Doctor Profit have revised their downside targets, saying the cycle bottom could hit a range between $44,000 and $54,000. However, the key question is whether the resolution of the immediate U.S. political risk will be enough to reverse these negative technical and on-chain trends, or if BTC is still vulnerable to a deeper test of support.
The post Here’s How US Funding Certainty Calmed Markets and Lifted Bitcoin appeared first on CryptoPotato.










 Adj. EPS: $2.71
Adj. EPS: $2.71 
 Revenue: $16.61B
Revenue: $16.61B  Net Income: $1.81B
Net Income: $1.81B Strong quarterly performance driven by double-digit revenue growth and solid profitability. pic.twitter.com/dy82pbdvOT
Strong quarterly performance driven by double-digit revenue growth and solid profitability. pic.twitter.com/dy82pbdvOT









